考虑定向能量沉积工艺特点的减材加工余量优化(3)
时间:2022-10-13 11:08 来源:未知 作者:admin 阅读:次
减材后处理的加工时间直观体现配准效果对加工效率的影响。鉴于实际加工过程中装夹、定位、换刀等辅助加工时间会影响实际有效加工时长的统计,故本文采用PowerMill仿真软件对比了案例余量优化前后有效加工时长(包括进刀、退刀及铣削加工时间)。减材加工采用PowerMill叶片加工策略,粗加工至余量2 mm,并以粗加工时间表征优化前后加工效率。减材加工参数设置如表4所示。配准后模型粗加工相比配准前少加工两道,时间缩短64 min 10 s,可见减材加工效率大幅度提高。
表4 PowerMill铣削粗加工仿真参数设置
2.4 验证分析
2.4.1 不同检测方案对余量优化影响
采用2.2节相同步骤优化以台阶效应波峰处测量点云为配准对象的加工余量,获得变换矩阵对比组Rcon、Tcon:

(9)
图15给出了对应余量优化结果,图16为配准后余量分布云图,可以看出余量分布相对均匀。图17给出了对比组配准后余量直方图信息,与图13b实验组配准结果相比,两组数据呈正态曲线分布且趋势相近,但对比组期望值μ更大,表明存在更多大余量区域。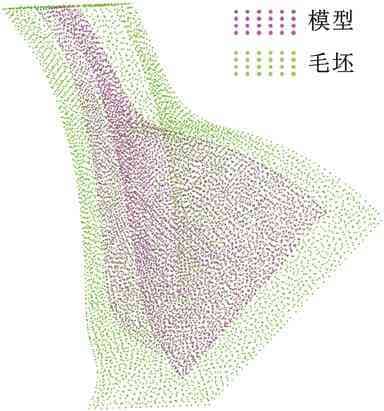
图15 对比组余量优化结果
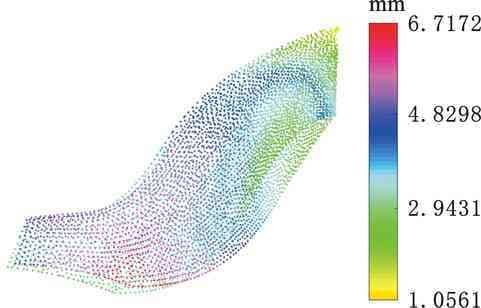
图16 对比组余量云图
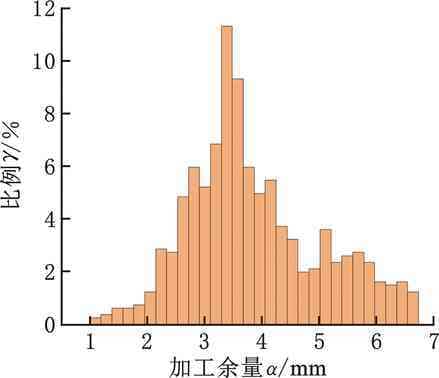
图17 对比组余量统计直方图
表5显示,相对于波谷实验组,波峰对比组余量均值dave增大0.3 mm,dmax增大0.89 mm。显然,波谷测点构建的外轮廓体积比波峰测点小。采用波峰处最大外轮廓配准,可能造成配准后局部区域实际加工余量为零或负余量,导致毛坯报废。另外,对比组S2值大于实验组S2值,说明对比组测点余量均匀性差。根据实际成形效果观测,制造凸起类缺陷(如局部黏附粉末、球化等)集中在波峰处。该类缺陷严重影响真实轮廓构建精度,进而影响余量优化结果。图18显示了DED毛坯上述缺陷。由于波峰处测点构建毛坯外轮廓更大,故理论粗加工多一道,时间增长31 min 28 s,实际最外层铣削仅接触波峰与凸起类缺陷处,存在大量空刀路。因此,波谷处构建的截面线不仅能精确反映最小外轮廓,且可减少制造缺陷引起的非真实轮廓测点数量,更适用于减材余量优化。
表5 不同在机检测方案余量统计结果
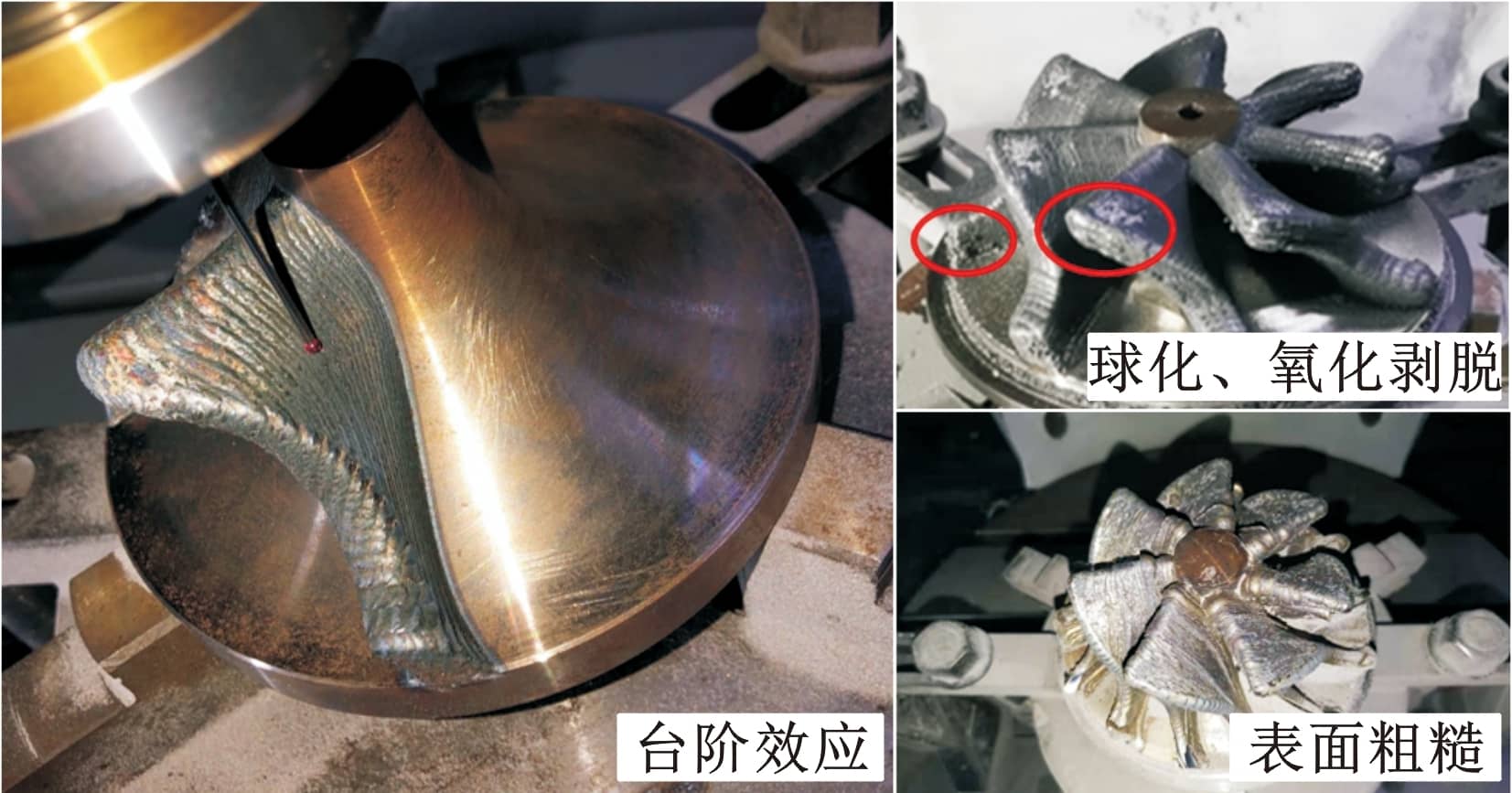
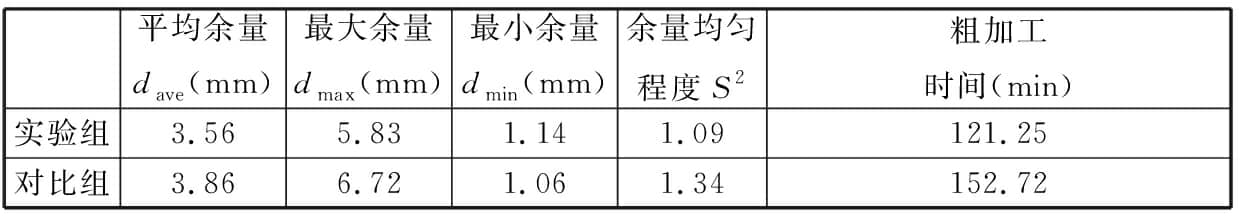

图18 激光定向沉积制造精度
2.4.2 不同配准方法对余量优化的影响为进一步验证本文所提余量优化算法的准确性,本节对比GAO等[16]提出的基于遗传算法(genetic algorithm,GA)的加工余量优化方法。该方法综合考虑了定位、均匀及外包络原则,目标函数统一为
min fGA=alg(efix(R,T)+bexp(S2(R,T)+
cexp(1-P(D(R,T)
(10)
上式等号右边三项分别对应定位、均匀及外包络原则,a、b和c为确定的权重系数。本文重新定义权重系数a=0.2、b=0.4、c=0.9,余量优化结果如图19与图20所示。
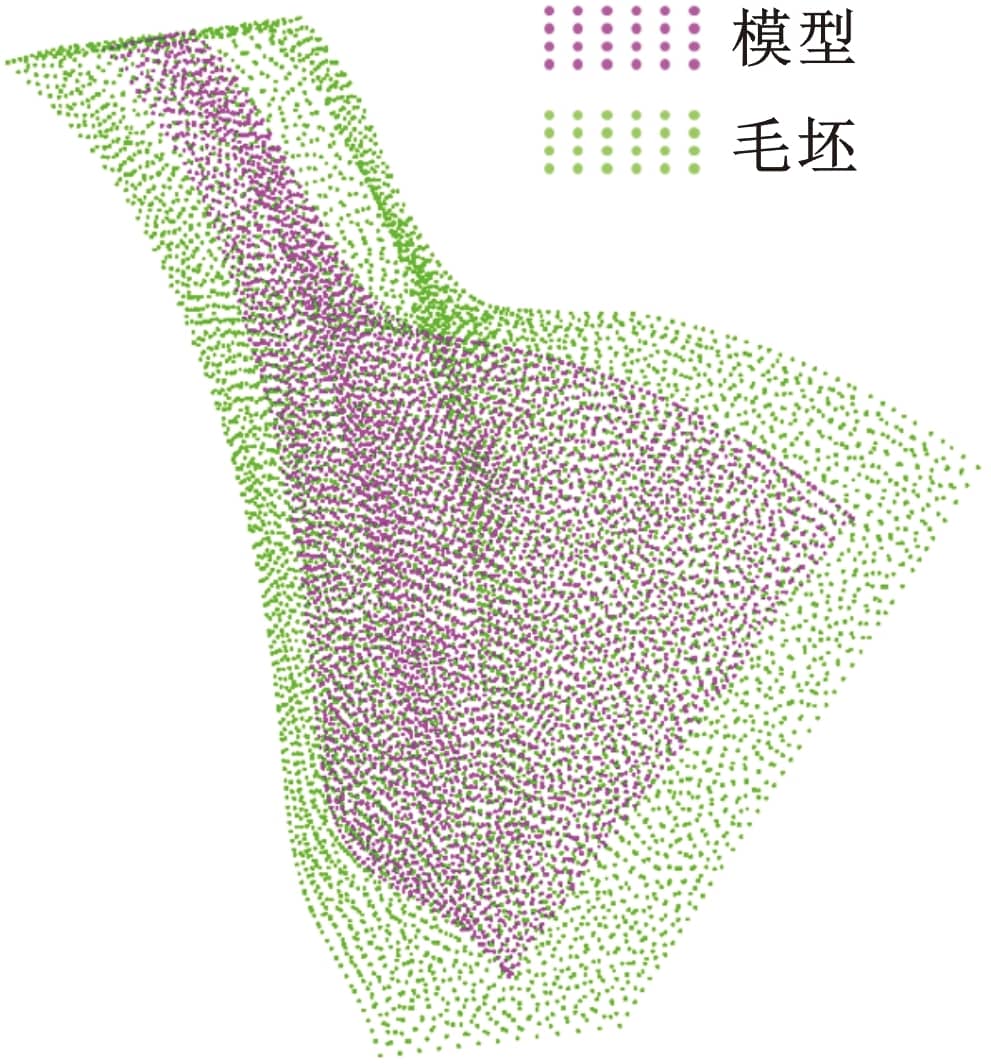
图19 GA余量优化方法余量优化结果
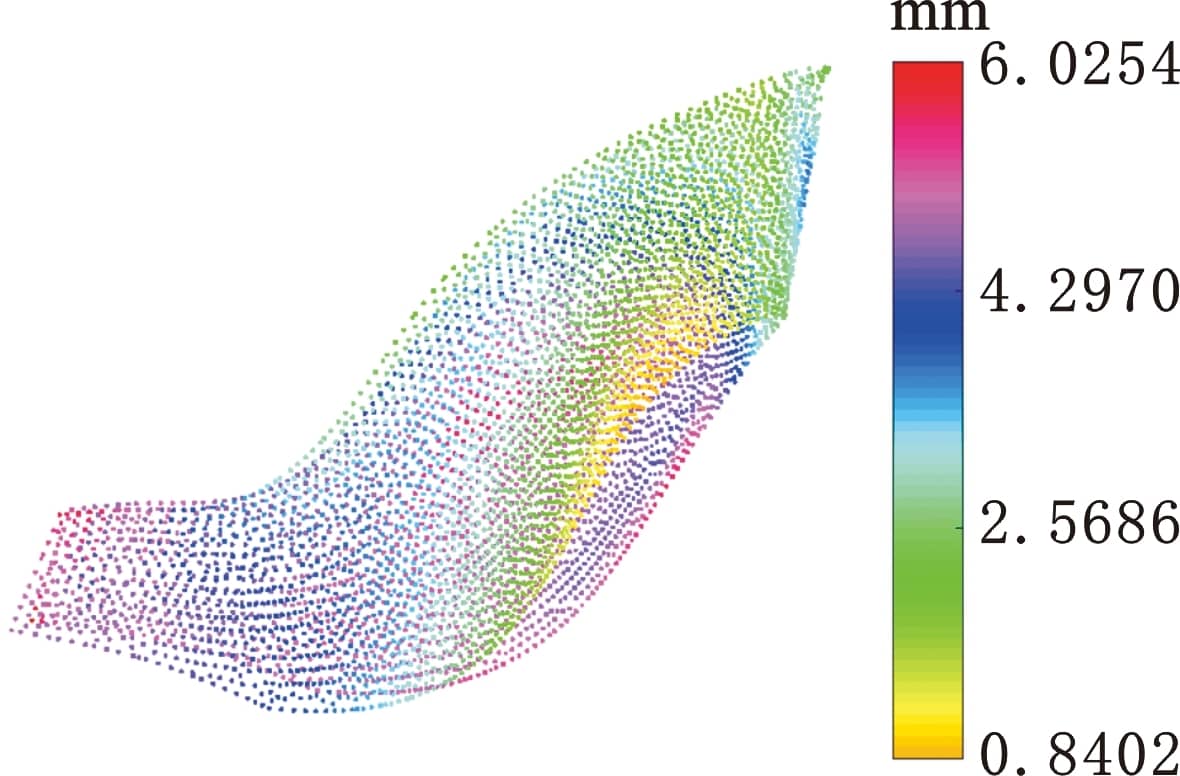
图20 GA余量优化方法余量云图
图21为上述方法余量优化结果直方图。相对于中面动态配准方法,GA优化后余量正态分布趋势不明显,效果不及所提方法。表6显示,该方法所得余量平均值为3.62
mm、最大值为6.02 mm、最小值为0.84 mm、方差值为1.69。对比本文所提方法,平均余量仅相差0.06 mm,但最大余量增加0.19
mm,最小余量减少0.3
mm,配准后理论加工时间也更长,余量优化后的粗加工效率明显不及所提方法。另外,需要指出,遗传算法是模拟染色体交叉、变异等优化求解,运算周期较长,而中面动态配准方法,因减少了点云数量且不采用随机求解,一般在几十秒即可完成计算。综上所述,所提方法综合性能优于GA余量优化方法。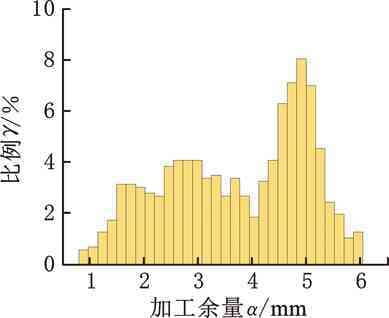
图21 GA配准方法余量统计直方图
表6 GA余量优化方法配准结果
3 结论
(1)所提在机检测截面线构建方法考虑了曲面类零件DED制造产生的台阶效应,利用台阶效应波谷位置准确构建叶片最小外轮廓,避免测量由制造缺陷构成的非真实外轮廓。余量优化结果表明所提截面线构建方法给出更大最小余量dmin及更小余量方差S2,可避免DED近净成形余量优化问题中局部余量不足现象。
(2)针对定位区域与待加工区域不同配准精度要求,引入动态权重因子平衡不同目标函数的博弈问题,同时,通过构造测量点云及理论模型点云中面,减少配准点云数量。相较于现有遗传算法余量优化技术,所提方法显著提高了余量优化效率。
(3)本文所提余量优化方法能快速优化DED毛坯与理论模型相对位置,均匀化减材加工后处理余量,可提高零件增减材复合加工效率并减小零件报废率。后续减材规划研究将进一步验证和讨论更复杂零件余量化后的效率提升效果。
参考文献:
[1] LIU S, SHIN Y C. Additive Manufacturing of Ti6Al4V Alloy:a Review[J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 164:1-23.
[2] 顾冬冬, 张红梅, 陈洪宇, 等. 航空航天高性能金属材料构件激光增材制造[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5):32-55.
GU Dongdong, ZHANG Hongmei, CHEN Hongyu, et al. Laser Additive Manufacturing of High-performance Metallic Aerospace Components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5):32-55.
[3] DEBROY T, WEI H L, ZUBACK J S, et al. Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Components-process, Structure and Properties[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 92:112-224.
[4] KARUNAKARAN K P, SURYAKUMAR S, PUSHPA V, et al. Low Cost Integration of Additive and Subtractive Processes for Hybrid Layered Manufacturing[J]. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2010, 26(5):490-499.
[5] MAYER T, BRNDLE G, SCHNENBERGER A, et al. Simulation and Validation of Residual Deformations in Additive Manufacturing of Metal Parts[J]. Heliyon, 2020, 6(5):e03987.
[6] BIKAS H, STAVROPOULOS P, CHRYSSOLOURIS G. Additive Manufacturing Methods and Modelling Approaches:a Critical Review[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 83(1/4):389-405.
[7] 曹著明, 孙红梅, 史海军. 某五轴数控加工中心在线检测关键技术研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2017(11):149-152.
CAO Zhuming, SUN Hongmei, SHI Haijun. The Research on the Key Technology of On-line Inspectionof a Five-axis NC Machining Center[J]. Machinery Design and Manufacture, 2017(11):149-152.
[8] AHN D, KWEON J H, KWON S, et al. Representation of Surface Roughness in Fused Deposition Modeling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech., 2009, 209(15/16):5593-5600.
[9] KAJI F, BARARI A. Evaluation of the Surface Roughness of Additive Manufacturing Parts Based on the Modelling of CUSP Geometry[J]. IFAC-Papers Online, 2015, 48(3):658-663.
[10] SHEN B, HUANG G Q, MAK K L, et al. A Best-fitting Algorithm for Optimal Location of Large-scale Blanks with Free-form Surfaces[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 139(1/3):310-314.
[11] LI X, LI W, JIANG H, et al. Automatic Evaluation of Machining Allowance of Precision Castings Based on Plane Features from 3D Point Cloud[J]. Computers in Industry, 2013, 64(9):1129-1137.
[12] SUN Y W, XU J T, GUO D M, et al. A Unified Localization Approach for Machining Allowance Optimization of Complex Curved Surfaces[J]. Precision Engineering, 2009, 33(4):516-523.
[13] 张莹, 刘敏, 张定华, 等. 基于在线检测的叶片加工余量自适应优化方法[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2014, 24(11):226-229.
ZHANG Ying, LIU Min, ZHANG Dinghua, et al. An Adaptive Approach for Machining Allowance Balancing for Blade Based on Online Measurement[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2014, 24(11):226-229.
[14] YING Z, ZHANG D, WU B. An Approach for Machining Allowance Optimization of Complex Parts with Integrated Structure[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2015, 2(4):248-252.
[15] 张明德, 马帅, 谢乐, 等. 大型船用螺旋桨自适应加工方法研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2019, 38(11):1752-1759.
ZHANG Mingde, MA Shuai, XIE Le, et al. Study on Adaptive Machining Method for Large Marine Propeller[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2019, 38(11):1752-1759.
[16] GAO Y Z, DU Z J, LI M Y, et al. An Automated Approach for Machining Allowance Evaluation of Casting Parts[J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2019, 32(11):1043-1052.
[17] 岳晶. 整体叶轮在机检测与加工余量优化技术研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2016.
YUE Jing. Research on On-machine Measuring and Allowance Optimization Technology of the Integral Impeller[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[18] 谭高山, 张涛, 张丽艳, 等. 基于动态精度评估机制的自适应定位方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2021, 27(12):3550-3558.
TAN Gaoshan, ZHANG Tao, ZHANG Liyan, et al. Adaptive Localization Method Based on Dynamic Accuracy Assessment Mechanism[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2021, 27(12):3550-3558.
[19] 王威振, 莫蓉, 万能. 叶片模型公差约束条件下的配准方法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2013, 49(10):264-266.
WANG Zhenwei, MO Rong, WAN Neng. Tolerance Zone Constrained Registration Method for Aeroengine Blade Models[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2013, 49(10):264-266.
[20] BESL P J, MCKAY N D. A Method for Registration of 3-D Shapes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2):239-256.
[21] 刘宇, 熊有伦. 基于有界K-D树的最近点搜索算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 36(7):73-76.
LIU Yu, XIONG Youlun. Algorithm for Searching Nearest-neighbor Based on the Bounded K-D Tree[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(7):73-76.
[22] ARUN K S, HUANG T S, BLOSTEIN S D. Least-squares Fitting of Two 3-D Point Sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1987, 9(5):689-700.
[23] 孔刘伟, 王振忠, 叶超, 等. 五轴增减材混合加工中心集成开发技术研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(6):53-59.
KONG Liuwei, WANG Zhenzhong, YE Chao, et al. Research on Developing Technology of Five-axis Additive-subtractive Hybrid Machining Center[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 62(6):53-59.
Subtractive Post-machining Allowance Optimization Considering Characteristics of DEDs
HOU Liang GUO Jing CHEN Yun YE Chao XU Yang ZOU Jiahao
Department of Mechanical and Electric Engineering,Xiamen University,Xiamen,Fujian,361005
Abstract: Complex free-form parts manufactured by DED had problems of uneven allowance distributions and severe stair-case effects. In order to optimize allowances for subtractive post-machining, a dynamic point cloud registration method using the mid-surface points of the deposited and theoretical parts was proposed to optimize the machining allowances, which took into consideration characteristics of the DED parts. Firstly, the section line of the minimum outer envelope of deposited complex free-form parts was constructed according to the deposition scanning path, and was used for obtaining the point cloud of the on-machine measurement. Secondly, the mid-surface points of the deposited and theoretical parts were extracted, and an iterative closest point with dynamic weights considering the multi-region allowance requirements was proposed to optimize the machining allowances. The feasibility of the algorithm was verified by two simple cases. Finally, a free-form blade of a centrifugal impeller was selected as a complex case for allowance optimization. The proposed method was also compared with the method for multi-region allowance using genetic algorithm. The results show that the proposed allowance optimization method is more accurate and efficient for rapid optimization of machining allowances for DED manufactured complex curved parts.
Key words: directed energy deposition(DED); allowance optimization; on-machine measurement; dynamic registration; stair-case effect
作者简介:侯 亮,男,1974年生,教授、博士研究生导师。研究方向为大批量个性化定制和增减复合制造等。发表论文197篇。E-mail:hliang@xmu.edu.cn。陈 云(通信作者),女,1987年生,助理教授。研究方向为增减复合制造、难加工材料切削机理、精密检测等。发表论文21篇。E-mail:yun.chen@xmu.edu.cn。
(责任编辑:admin)
相关内容
最新内容
热点内容

 梁柏涛:美国参议院这一票
梁柏涛:美国参议院这一票 美国俄亥俄州宣布拨款6200
美国俄亥俄州宣布拨款6200 Schunk集团全资收购ESK-SI
Schunk集团全资收购ESK-SI 美国空军利用拓竹3D打印机
美国空军利用拓竹3D打印机 3D Systems推出集成式数字
3D Systems推出集成式数字 Aker Solutions设立新3D打
Aker Solutions设立新3D打 GoEngineer通过收
GoEngineer通过收 3D食品打印:烹
3D食品打印:烹 卡内基梅隆研究人
卡内基梅隆研究人 Align Technology
Align Technology AM Craft在种子轮
AM Craft在种子轮 Aerojet拿下五角
Aerojet拿下五角

